
PostgreSQL
e' un potente DBMS relazionale Open Source noto per
la robustezza e la ricchezza di funzionalita'.
Questo documento descrive il modulo aggiuntivo Statspack
che consente la raccolta e la memorizzazione delle statistiche prestazionali di PostgreSQL.
Il documento fa riferimento alla versione 9.2
di PostgreSQL su Linux ma e', mutatis mutandis, valido anche per le altre versioni.
Un documento introduttivo su PostgreSQL e' Introduzione a PostgreSQL, un documento piu' completo e' Qualcosa in piu' su PostgreSQL, le statistiche prestazionali in PostgreSQL sono un prerequisito per la lettura di questa pagina.
E' stato sviluppato per PostgreSQL uno strumento che consente l'esecuzione di snapshot delle statistiche della base dati ed il loro confronto: pgStatsPack. La funzionalita' e' simile allo Statspack introdotto nella base dati Oracle dalla versione 8.1.6 e quindi aggiornato con l'AWR. pgStatsPack e' mantenuto su PgFoundry, il sito del gruppo di sviluppo di PostgreSQL per la pubblicazione di software PostgreSQL non compreso nel core. pgStatsPack e' implementato con una serie di script SQL e Bourne shell di facile manutenzione.
In pratica pgStatsPack raccoglie e mantiene le principali statistiche di PostgreSQL (pg_stat_XXX e pg_statio_XXX) consentendo un'analisi temporale e non solo dell'ultima situazione presente.
Installare lo statspack per PostgreSQL richiede pochi veloci passi:
Results for database PGDBS01 Installing Statistics Package for database PGDBS01 Results for database PGDBS02 Installing Statistics Package for database PGDBS02 ...
*/20 * * * * /var/lib/pgsql/pgstatspack/bin/snapshot.sh >> /tmp/pgstat.log 2>&1 5 3 * * * /var/lib/pgsql/pgstatspack/bin/delete_snapshot.sh > /tmp/pgstat.log 2>&1
pgstatspack_report.sh [username] [database]
E' possibile effettuare snapshot a richiesta, per esempio prima e dopo l'esecuzione di
un batch da analizzare, utilizzando la funzione
select pgstatspack_snap('Nome Snapshot');.
L'installazione crea una serie di tabelle public.pgstatspack_XXX che contengono i dati raccolti
dalle viste di sistema pg_stat_XXX con snap_id sequenziali. Se la vista pg_stat_statements,
descritta nel paragrafo precedente, e' presente viene anch'essa campionata.
Le tabelle sono mantenute nello schema public e sono ovviamente interrogabili con l'SQL.
Le query piu' interessanti sono contenute nel report pgstatspack_report.sh e
queste possono studiate e modificate liberamente.
La prima parte dello script e' interattiva e richiede all'utente di specificare
gli estremi degli snapshot da analizzare, quindi vengono eseguite una serie di query
che riportano le attivita' eseguite nell'intervallo di tempo scelto.
La seguente query di esempio riporta per ogni database il Throughput, l'Hit Ratio, le letture logiche,
le letture fisiche ed i rollback al secondo nell'intervallo di tempo selezionato:
PSQL="psql"
PGUSER="postgres"
PGDB=PGTST01
STARTSNAP=140
STOPSNAP=141
$PSQL --user $PGUSER --dbname $PGDB --quiet --command "
SELECT a.datname as database,
round(CAST ( ((b.xact_commit-a.xact_commit)
/(select EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM (d.ts-c.ts)) from pgstatspack_snap c, pgstatspack_snap d
where c.snapid=$STARTSNAP and d.snapid=$STOPSNAP)) AS numeric),2) as tps,
round(CAST ((100*(b.blks_hit-a.blks_hit)/((b.blks_read-a.blks_read)+(b.blks_hit-a.blks_hit+1))) AS numeric),2) as hitrate,
round(CAST ( (((b.blks_read-a.blks_read)+(b.blks_hit-a.blks_hit))
/(select EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM (d.ts-c.ts)) from pgstatspack_snap c, pgstatspack_snap d
where c.snapid=$STARTSNAP and d.snapid=$STOPSNAP)) AS numeric),2) as lio_ps,
round(CAST ( ((b.blks_read-a.blks_read)
/(select EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM (d.ts-c.ts)) from pgstatspack_snap c, pgstatspack_snap d
where c.snapid=$STARTSNAP and d.snapid=$STOPSNAP)) as numeric),2) as pio_ps,
round(CAST ( ((b.xact_rollback-a.xact_rollback)
/(select EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM (d.ts-c.ts)) from pgstatspack_snap c, pgstatspack_snap d
where c.snapid=$STARTSNAP and d.snapid=$STOPSNAP)) as numeric),2) as rollbacks_ps
FROM pgstatspack_database_v a, pgstatspack_database_v b
WHERE a.snapid=$STARTSNAP
AND b.snapid=$STOPSNAP
AND a.datname=b.datname
ORDER BY tps desc;"
Vediamo ora un esempio di report generato:
Using file name: /tmp/pgstatreport_PGPRD01_730_740.txt
#################################################################################################
PGStatspack version 2.3.2 by uwe.bartels@gmail.com
#################################################################################################
Snapshot information
Begin snapshot :
snapid | ts | description
--------+----------------------------+---------------------
720 | 2012-02-09 13:00:01.736479 | cron based snapshot
End snapshot :
snapid | ts | description
--------+----------------------------+---------------------
730 | 2012-02-09 16:20:01.427012 | cron based snapshot
Seconds in snapshot: 11999.690533
Database version
version
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PostgreSQL 9.0.4 on x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu, compiled by GCC gcc (GCC) 4.1.2 20080704 (Red Hat 4.1.2-48), 64-bit
Database information
current_database | dbsize
------------------+--------
PGPRD01 | 254 GB
Database statistics
database | tps | hitrate | lio_ps | pio_ps | rollbk_ps
-----------+------+---------+--------+--------+-----------
PGPRD01 | 9.96 | 99.00 | 924.04 | 21.01 | 0.10
postgres | 0.04 | 99.00 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.00
template0 | 0.03 | 99.00 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.00
template1 | 0.03 | 99.00 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.00
Top 20 tables ordered by table size changes
table | table_growth | index_growth
--------------------------------------+--------------+--------------
demo001.tab_001_config | | 0
public.pgstatspack_database | | 8192
pg_toast.pg_toast_1099899 | | 0
...
Top 20 tables ordered by high table to index read ratio
table | system_read_pct | table_read_pct | index_read_pct
-------------------------------------+-----------------+----------------+----------------
demo001.tab_001_apparecchiatura | 42 | 99 | 0
demo001.tab_001_unita_immobiliare | 25 | 100 | 0
demo001.tab_001_rapp_dettaglio | 9 | 99 | 0
...
Top 20 tables ordered by inserts
table | table_inserts
-----------------------------------+---------------
public.pgstatspack_indexes | 4030
public.pgstatspack_tables | 3240
public.pgstatspack_sequences | 600
...
Top 20 tables ordered by updates
table | table_updates
-----------------------------------+---------------
demo001.tab_001_rapp_controllo | 66
bench0.transazione | 43
demo001.tab_001_rapp_dettaglio | 41
...
Top 20 tables ordered by deletes
table | table_deletes
--------------------------------------+---------------
appl_prd.analisi_richieste | 2
appl_prd.analisi_dati | 1
demo001.tab_001_apparecchiatura | 1
...
Tables ordered by percentage of tuples scanned
table | rows_read_pct | tab_hitrate | idx_hitrate | tab_read | tab_hit | idx_read | idx_hit
---------------------------------------+---------------+-------------+-------------+----------+---------+----------+---------
demo001.tab_001_apparecchiatura | 42 | 99 | 99 | 0 | 988801 | 0 | 284
demo001.tab_001_unita_immobiliare | 25 | 99 | 98 | 0 | 311408 | 0 | 66
demo001.tab_001_rapp_dettaglio | 9 | 99 | 99 | 4 | 268576 | 0 | 228
...
Indexes ordered by scans
index | table | scans | tup_read | tup_fetch | idx_blks_read | idx_blks_hit
------------------------------------------------+----------------------------------+-------+----------+-----------+---------------+--------------
appl_prd.xpktracciatura | appl_prd.tracciatura | 61841 | 61852 | 61852 | 0 | 123928
pg_catalog.pg_attribute_relid_attnum_index | pg_catalog.pg_attribute | 13663 | 37109 | 37109 | 0 | 28069
pg_catalog.pg_class_oid_index | pg_catalog.pg_class | 9958 | 9956 | 9956 | 0 | 20569
...
Sequences ordered by blks_read
sequence | blks_read | blks_hit
---------------------------------------+-----------+----------
demo001.seq_tab_001_apparecchiatura | 0 | 25
demo001.seq_tab_001_bollino | 0 | 6
...
Top 20 SQL statements ordered by total_time
calls | total_time | total_time_percent | rows | user | query
-------+------------+--------------------+------+------+-------
Top 20 user functions ordered by total_time
funcid | function_name | calls | total_time | self_time
--------+---------------+-------+------------+-----------
background writer stats
checkpoints_timed | checkpoints_req | buffers_checkpoint | buffers_clean | maxwritten_clean | buffers_backend | buffers_alloc
-------------------+-----------------+--------------------+---------------+------------------+-----------------+---------------
40 | 0 | 1723 | 0 | 0 | 169 | 170
background writer relative stats
checkpoints_timed | minutes_between_checkpoint | buffers_checkpoint | buffers_clean | buffers_backend | total_writes | avg_checkpoint_write
-------------------+----------------------------+--------------------+---------------+-----------------+--------------+----------------------
100% | 5 | 91% | 0% | 8% | 0.001 MB/s | 0.000 MB
activity stats
current_sessions | current_active_sessions | old_sessions | old_active_sessions | delta_sessions | delta_active_sessions
------------------+-------------------------+--------------+---------------------+----------------+-----------------------
18 | 1 | 26 | 1 | -8 | 0
Parameters
name | start_setting | stop_setting | source
------------------------------+-------------------------------+-------------------------------+----------------------
max_stack_depth | 2048 | 2048 | environment variable
hba_file | /pgdata1/data/pg_hba.conf | /pgdata1/data/pg_hba.conf | override
...
This report is saved as /tmp/pgstatreport_PGPRD01_730_740.txt
Poiche' il pacchetto non veniva piu' mantenuto... ho aggiornato di pg_statspack per renderlo compatibile alla versione 9.2 e per raccogliere i dati anche dalla vista di sistema pg_stat_activity. La versione 2.3.2 dispone in tal modo anche di informazioni sul numero di sessioni e sugli utenti (pgStatsPack 2.3.2). Sfruttando la raccolta a tempo dei dati e' possibile produrre grafici molto significativi come quelli di pg2ch:

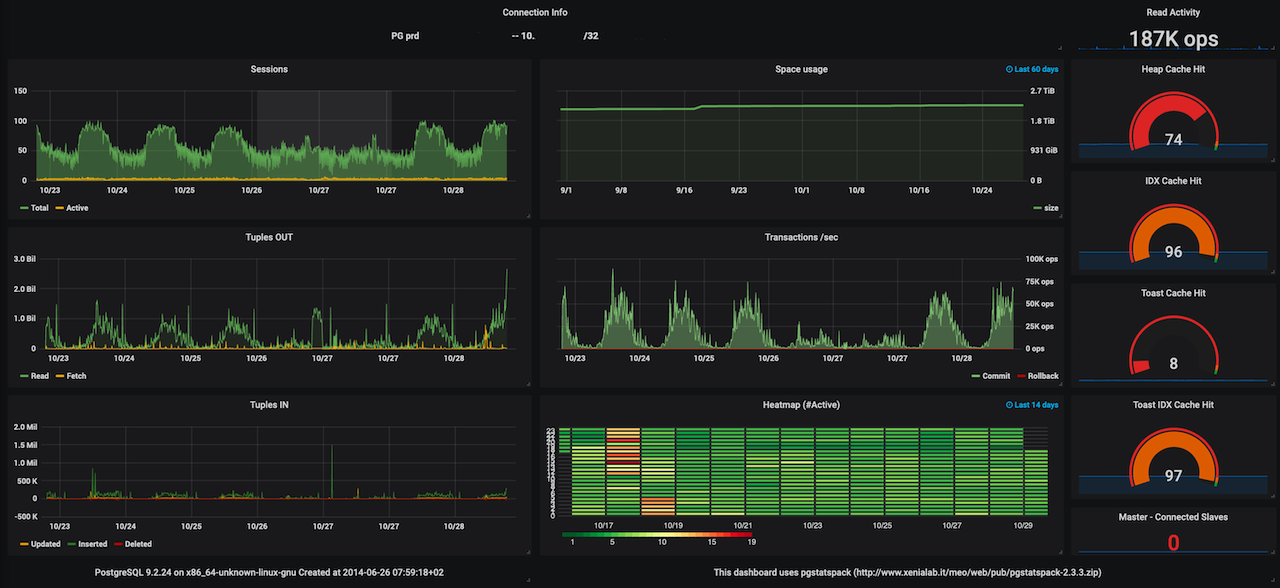
La versione 2.3.3 di pg_statspack raccoglie ulteriori dati, e' compatibile con le ultime versioni PostgreSQL 9.6, 10, 11 e 12 (pgStatsPack 2.3.3). Inoltre utilizza per default una raccolta dati ridotta ma efficiente per la visualizzazione di grafici con Grafana:
Titolo: PostgreSQL Statspack
Livello: Avanzato
Data:
14 Febbraio 2015
Versione: 1.0.4 - 31 Ottobre 2019 🎃 Halloween
Autore: mail [AT] meo.bogliolo.name